Smoothing or Averaging filter in Spatial Domain
hive-169321·@biggestloser·
0.000 HBDSmoothing or Averaging filter in Spatial Domain
<center><h1>Spatial Domain</h1></center>
___
Spatial Domain can be broadly said as the image space. The image can be represented in the form of a 2D matrix where each element of the matrix represents pixel intensity. This state of 2D matrices which depict the intensity is called Spatial Domain. Manipulation of the pixel values are done here and the image is processed pixel by pixel.
___
<center><h2>Smoothing Filter</h2></center>
___
Image smoothing is a digital image processing technique that reduces and suppresses image noises. In the spatial domain, neighborhood averaging can generally be used to achieve the purpose of smoothing.
___
<center><h2>Average Filter</h2></center>
___
Average filtering is a method of **smoothing** images by reducing the amount of intensity variation between neighbouring pixels. The average filter works by moving through the image pixel by pixel, replacing each value with the average value of neighbouring pixels, including itself.
___
<center><h2>Program</h2></center>
___
### Importing python libraries
>import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
### Reading the image
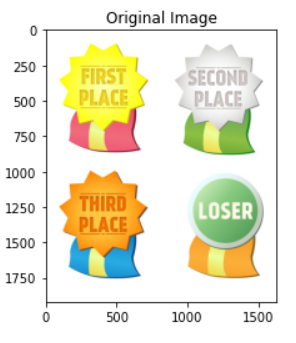
>image = cv2.imread('badges.jpg')
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
plt.title('Original Image')
plt.imshow(image);
### Converting the original image to grayscale
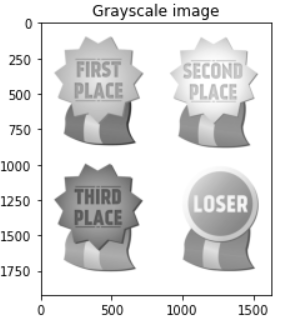
>img = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
plt.title('Grayscale image')
plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray', vmin=0, vmax=255);
### Number of rows and columns of the image
>m, n = img.shape
print(f'Rows: {m}, Columns: {n}')
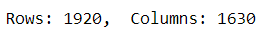
### Developing Averaging filter mask of (3,3)
##### _If the image is bigger in size then you can increase the mask to (5,5) or (7,7)._
>mask = np.ones([3,3], dtype=int)
mask = mask/9
print(mask)

### Convolving the 3X3 mask over the image
>newImage = np.zeros([m, n])
print(newImage)


___
**Median Filter:** Median filtering is a nonlinear process useful in reducing impulsive, or salt-and-pepper noise. In a median filter, a window slides along the image, and the median intensity value of the pixels within the window becomes the output intensity of the pixel being processed.
___
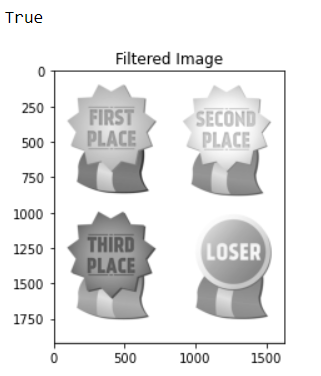
### Traverse the image. For every 3X3 area, The median of the pixels are found and center pixel of the median is replaced by it.
___
**Tools Used: Jupyter NoteBook
Python Libraries: OpenCV, numpy, matplotlib**
___
<center><h2>Explanation</h2></center>
___
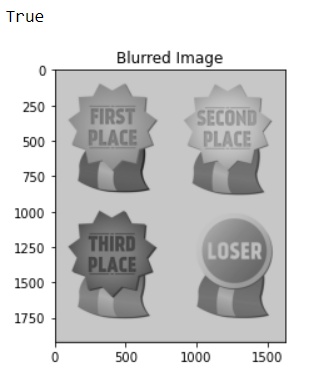
_The original image is taken into the imread function of OpenCv and is displayed in the output with the help of matplotlib. The image is converted into grayscale for further process. The number of rows and columns of the image are obtained by the shape function which comes out to be 480 rows and 640 columns. A 3x3 averaging filter is generated containing all elements as 1 and it is divided by 9. The 3x3 mask created are convolved over the image. The blurred image is created through the imwrite() function of OpenCV and is stored in the workspace of jupyter notebook. It is observed that the filtered image is slightly blurred. If we increase the size of the averaging mask, more blurring can
be obtained. For median filtering the image is traversed for every 3x3 area. The median of the pixels is found out and the center is replaced by the median. The median filtered image is considerably enhanced with hardly any salt and pepper noise in it._
**Conclusion:**
1. It is observed that the filtered image is slightly blurred. If we increase the size of the averaging mask, more blurring can be obtained.
2. The median filtered image is considerably enhanced with hardly any salt and pepper noise in it.
___
**References:** Wikipedia, geeksforgeeks website, personal prepared notes.
<a href='https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spatial_filter'>Reference 1</a> <a href='https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Smoothing'>Reference 2</a> <a href='https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/spatial-filtering-and-its-types/'>Reference 3</a>
**Image Source:** https://pixabay.com
___
### I tried to make the code simple to understand and gave explanation of the various functions used in the program. Feel free to give your suggestions. Until we meet again in some other post, this is @biggestloser signing off....
___
<center>

</center>👍 gangstalking, sqube, ctime, voter, lerkfrend, arcange, raphaelle, fengchao, laruche, walterjay, hive-143869, stayten, hive-134220, discovery-it, gianluccio, ciuoto, carolineschell, pab.ink, piumadoro, mad-runner, vittoriozuccala, lycos, oscurity, phage93, mariluna, middleearth, adinapoli, akireuna, titti, maryincryptoland, libertycrypto27, tinyhousecryptos, medussart, axel-blaze, discovery-blog, riccc96, ghastlygames, meppij, matteus57, filosbonus1, yggdrasilwind, spiceboyz, marcolino76, sbarandelli, a0i, spaghettiscience, jesusmedit, lallo, david.steem, stregamorgana, meeplecomposer, claudietto, delilhavores, hjmarseille, jennyzer, mengene, peterpanpan, divadstrokes, sarita3, mattbrown.art, armandosodano, investegg, knfitaly, ilovecanada, onelovedtube, yusmi, originalmrspice, scottshots, d00k13, mrchef111, illuminationst8, melor9, icepee, zainenn, davixesk8, zeruxanime, minnowsupport, amberyooper, activate.alpha, warpedpoetic, victoriabsb, zaxan, paolazun, clayboyn, chicoduro, fundacoven, doodle.danga, crimsonclad, anarcist69, blarchive, anarcist, serialfiller, angelica7, cooperfelix, followbtcnews, donatello, devann, brainpod, st3llar, adventuroussoul, jeronimorubio, deepsouthpiddlin, camuel, elvys, tonysayers33, pauliinasoilu, tipy, joseluis91, hivebuzz, steemitboard, holovision.stem, yggdrasil.laguna, stemgeeks, stemcuration, brofund-stem, adamada.stem, stemline, star.stem, babytarazkp, scooter77.stem, zorg67, emrebeyler.stem, limka, mundo.curioso, tonimontana, scientician, stemcur, zdigital222, flsfserkan, krishu.stem, solominer.stem, kohsamui99, abh12345.stem, cd-stem, pfwaus, dorkpower, meestemboom, juecoree.stem, rikarivka, an-man, bearbear613, rafaelaquino,