Philosophy Of Science🌍
philosophy·@petermichael·
0.000 HBDPhilosophy Of Science🌍
Philosophy as we know is the study of fundamental nature of knowledge, reality n existence especially when considered as academic discipline. But this Philosophy we are talking about, How? And what is the history about?. Let's find out! The history of the philosophy of science, certainly in the Western world, begins with the philosophers of Ancient Greece. Whilst many other philosophers contributed to the very beginning of the scientific process, the genesis of science began with the contrast between Platonism and Aristotleism. Plato (428/427 BC[a] - 348/347 BC) had the archetypal Greek belief, that humanity was born with an innate knowledge of everything, and that learning was a process of unlocking the memories. His argument was that everything had a perfect potential abstract form, and that any knowledge gained through observation and experiment was filtered by the senses. Empirical knowledge, according to Plato, was mere opinion. Therefore, he reasoned, that pure knowledge could be advanced by deduction alone. Aristotle (384 - 322 BCE), by contrast, believed that Plato had everything the wrong way around, and that knowledge could only be gained by comparing it with what was already known and perceived. 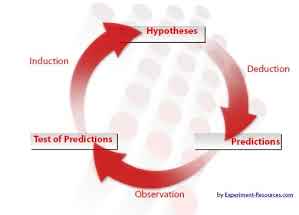 For example, Plato's famous idealized Republic required a perfect Philosopher King to rule it, with wisdom and benevolence. He argued that because such a perfect human being could exist, therefore such a king would be possible to find. Aristotle countered this concept by stating that because he had never seen or heard of such a human in recorded history, then it was an impossible concept. He believed that inductive reasoning was required to establish some basic premises before scientific demonstrations. Between the two schools of thought, the idea of deductive reasoning emerged, which has remained a cornerstone of the scientific method. This idea remained a common theme throughout the history of philosophy of science.