Java Variables For Day 4 Of 30 Days Of Java
java·@run.vince.run·
0.000 HBDJava Variables For Day 4 Of 30 Days Of Java
<h3>When Will The Progress Stop</h3>
[Image not Java but courtesy of pexels.com](pexels.com)
I know I’m not going to be able to keep this up forever. Sooner or later my progress is going to stop. For now I hope I’m still making sense with what I’m posting. So let’s not delay and get my day 4 update out.
<h2>What Did I Learn Today</h2>
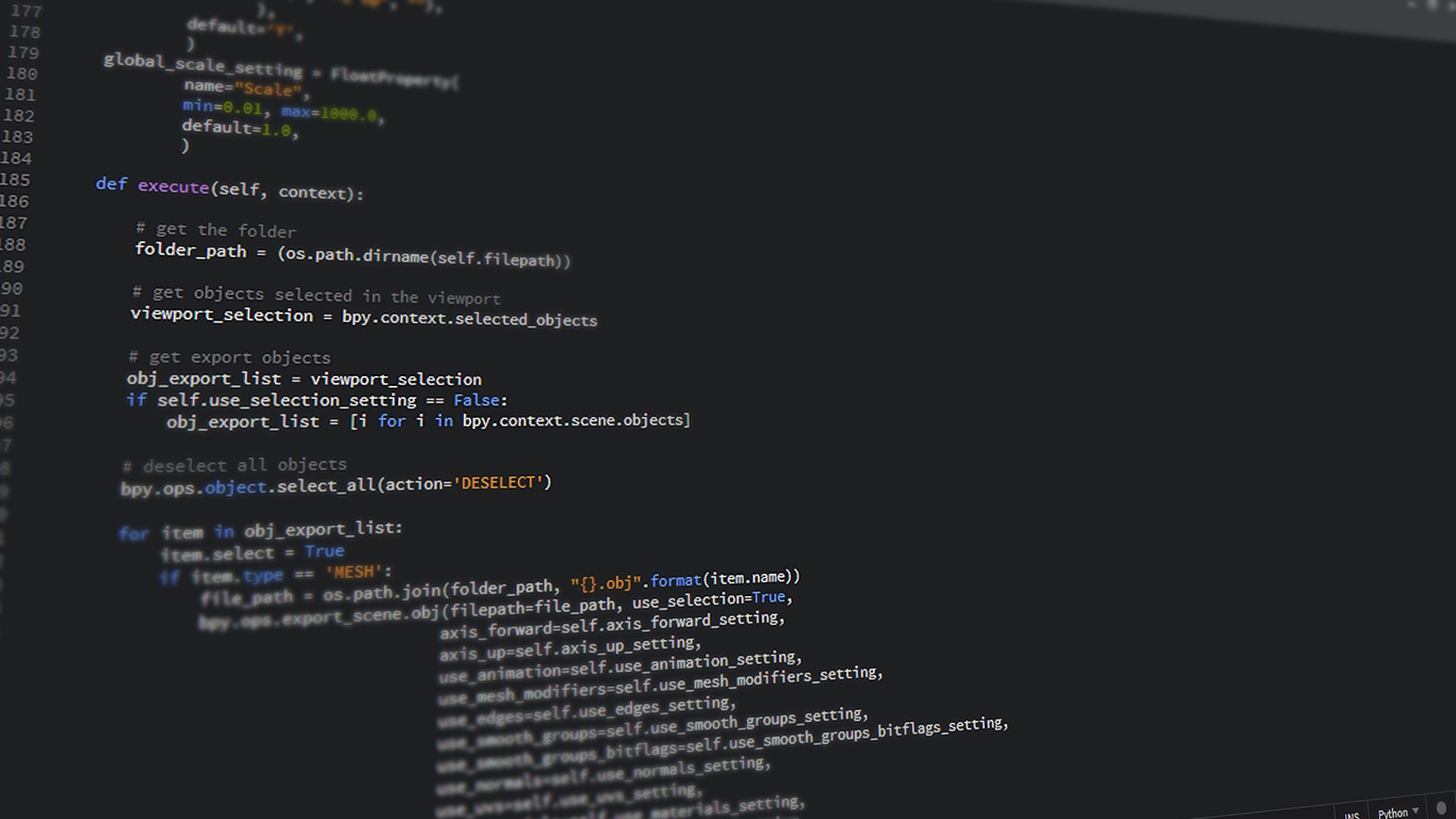
- Java Variables: Variable is a name associated with a value that can be changed. Specifically, we name the address of where the value is stored in memory, instead of having to remember the complex memory address. When you declare a variable in java you need to specify the data type as well as the variable name, eg: int i = 10;
So declaring a variable
```data_type variable_name = value;```
You can also declare the variable and then assign a value
```int i;```
```i = 100;```
- Variable Naming Conventions: Variables names need to adhere to a set of standards during your code and these include.
1. Variables cannot start with white space
2. Variables can begin with a special character
3. Variable names should start with a lowercase and second words should start with a capital letter
4. Variable names are case sensitive
- There are 3 types of Variables in Java:
1. Static or class variables: they are associated with the class and common for all instances of class. If you create an object from a class, the variable would be the same for each object. A static variable remains constant and cannot be changed. When declaring the variable you use the word static before declaring the variable, eg: public static String variableName="Variable";
2. Instance Variable: Instance variables are declared inside a class but outside and member, constructor of class. Each object has their own copy of the variable.
3. Local Variable: Variable declared inside the method of the class and their scope is limited to the method which means you can't change the variable or access them outside the method.
<h2>Code For The Day</h2>
Below is a sample program illustrating the use of Static, Instance and Local variables:
```
public class VariableExample {
// instance variable
public String myVar="instance variable";
public void myMethod(){
// local variable
String myVar = "Inside Method";
System.out.println(myVar);
}
public static void main(String args[]){
VariableExample obj = new VariableExample();
System.out.println("Calling Method");
obj.myMethod();
System.out.println(obj.myVar);
}
}
```
Output
```
$ java VariableExample
Calling Method
Inside Method
instance variable
```
<h3>I'll be posting daily, sharing my experiences on my “1 Month of Java Code” experiences”, my previous post on day 3 can be found below, so feel free to have a look:
https://steemit.com/java/@run.vince.run/day-3-of-javatober-and-learning-what-the-jvm-is</h3>
<h3>If you have found this post useful or interesting, please consider Commenting, Upvoting, Following and/or Resteeming</h3>👍 ilovecoding, anzub, apshamilton, runburgundy, runningproject, plantstoplanks, primersion, byebyehamburgers, choogirl, teamaustralia, aussieninja, gohba.handcrafts, toofasteddie, maujmasti, freemon, run.vince.run, msp-active, centerlink, mikepedro, webcoop, cryptwo, onethousandwords, revo, melbourneswest, cryptoslicex, sue-stevenson, lifeobserver, masterwu, bec-on-the-block, philippekiene, niouton, jk6276, terrylovejoy, deividluchi, bernardwest, positiveninja2, ausbitbank, gamersclassified, sapphic, benleemusic, bobdos, metametheus, chrisdavidphoto, newtechblog,