SECURITY ATTACKS | Cryptographic attacks | SECURITY MECHANISMS
security·@shubhamupadhyay·
0.000 HBDSECURITY ATTACKS | Cryptographic attacks | SECURITY MECHANISMS
There are four general categories of attack which are listed below. **Interruption** An asset of the system is destroyed or becomes unavailable or unusable. This is an attack on availability e.g., destruction of piece of hardware, cutting of a communication line or Disabling of file management system **Interception** An unauthorized party gains access to an asset. This is an attack on confidentiality. Unauthorized party could be a person, a program or a computer.e.g., wire tapping to capture data in the network, illicit copying of files 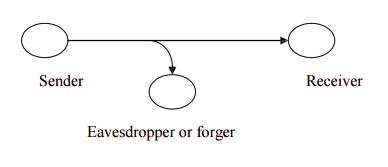 **Modification** An unauthorized party not only gains access to but tampers with an asset. This is an attack on integrity. e.g., changing values in data file, altering a program, modifying the contents of messages being transmitted in a network. 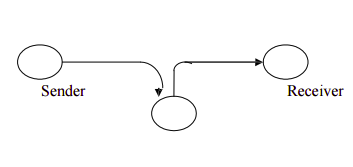 **Fabrication** An unauthorized party inserts counterfeit objects into the system. This is an attack on authenticity. e.g., insertion of spurious message in a network or addition of records to a file. 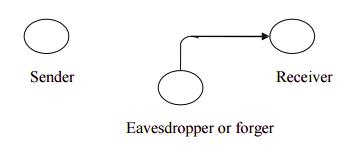 ### Cryptographic Attacks **Passive Attacks ** Passive attacks are in the nature of eavesdropping on, or monitoring of, transmissions. The goal of the opponent is to obtain information that is being transmitted. Passive attacks are of two types: **Release of message contents:** A telephone conversation, an e-mail message and a transferred file may contain sensitive or confidential information. We would like to prevent the opponent from learning the contents of these transmissions. **Traffic analysis: ** If we had encryption protection in place, an opponent might still be able to observe the pattern of the message. The opponent could determine the location and identity of communication hosts and could observe the frequency and length of messages being exchanged. This information might be useful in guessing the nature of communication that was taking place. Passive attacks are very difficult to detect because they do not involve any alteration of data. However, it is feasible to prevent the success of these attacks. **Active attacks** These attacks involve some modification of the data stream or the creation of a false stream. These attacks can be classified in to four categories: **Masquerade** – One entity pretends to be a different entity. **Replay** – involves passive capture of a data unit and its subsequent transmission to produce an unauthorized effect. **Modification of messages** – Some portion of message is altered or the messages are delayed or recorded, to produce an unauthorized effect. **Denial of service** – Prevents or inhibits the normal use or management of communication facilities. Another form of service denial is the disruption of an entire network, either by disabling the network or overloading it with messages so as to degrade performance. It is quite difficult to prevent active attacks absolutely, because to do so would require physical protection of all communication facilities and paths at all times. Instead, the goal is to detect them and to recover from any disruption or delays caused by them. ### SECURITY MECHANISMS One of the most specific security mechanisms in use is cryptographic techniques. Encryption or encryption-like transformations of information are the most common means of providing security. Some of the mechanisms are 1 Encipherment 2 Digital Signature 3 Access Control
👍 shubhamupadhyay, elliotjgardner, banjo, minnowsupport, pharesim, hitmeasap, raymondspeaks, krystle, jsantana, heretickitten, starrkravenmaf, fronttowardenemy, sidwrites, abcdoctor, qwasert, lenscape, stuntworks, ausbitbot, gpenco, cloh76, diana.catherine, zeartul, kralizec, jhermanbeans, worldtraveler, gre3n, pomperipossa, gbenga, singa, numpypython, choogirl, jhagi.bhai, marcusxman, gindor, whatamidoing, shawnfishbit, taica, oceancoinz, mrwanderlust, rootingrobert, glex, therv, steemcleaners, blacklist-a,