Comets - A Brief Primer
steemstem·@terrylovejoy·
0.000 HBDComets - A Brief Primer
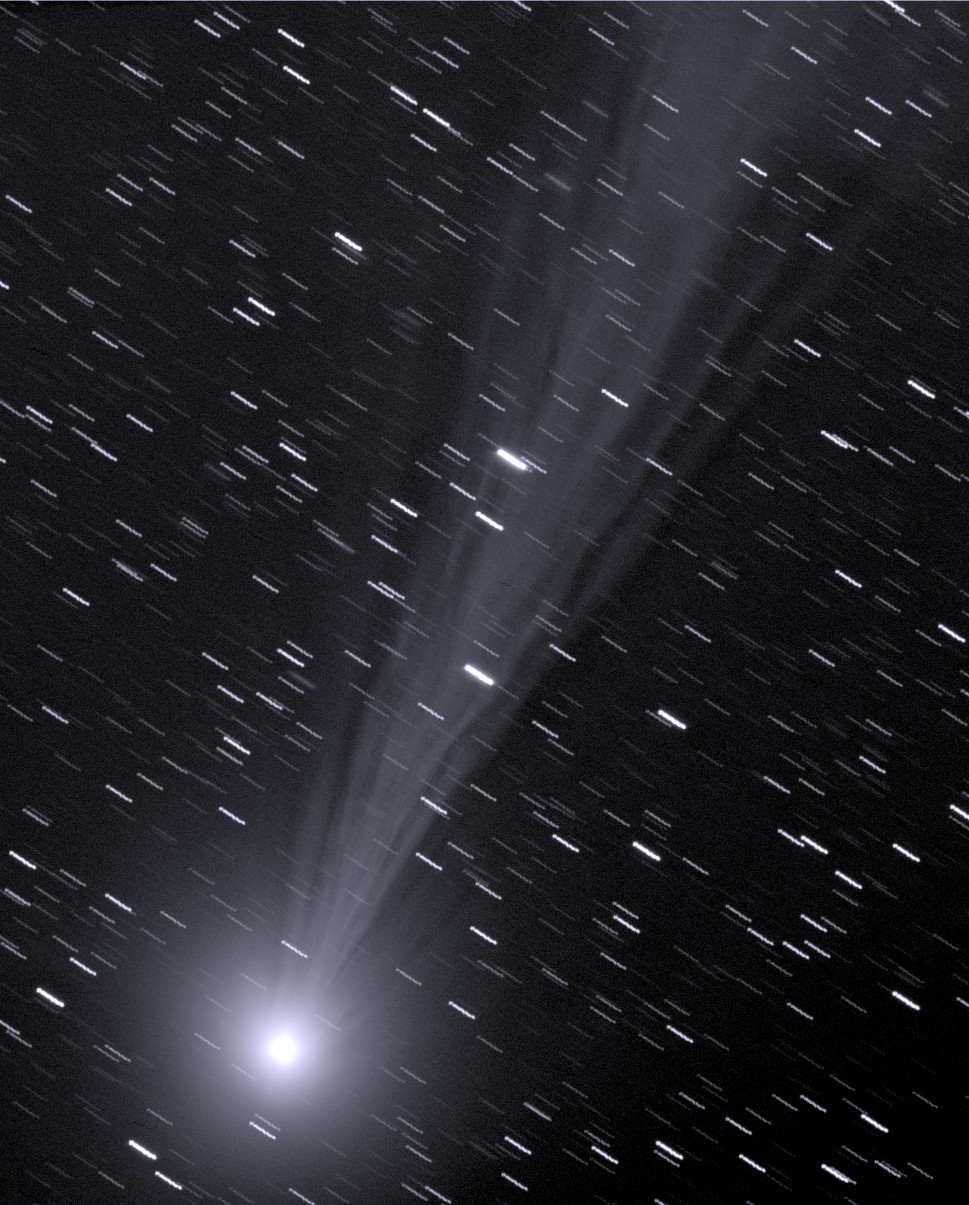 <center>*Comet C/2014 Q2 (Lovejoy) discovered by the author on August 17, 2014, had developed a complex ion tail shown here. This photo was a total of 510 seconds exposure using a Celestron C14, with a QHY9 camera and Hyperstar reducer on January 8, 2015*</center> One of the most beautiful sights in the night sky is the appearance of a bright comet that is visible to the naked eye. It is a rare event that occurs maybe once in a decade. Centuries ago, well before man-made light pollution, the appearance of a large comet could instill fear in many cultures and some believed them to be omens of war. William Shakespeare even wrote in his play Julius Caesar, "When beggars die there are no comets seen; The heavens themselves blaze forth the death of princes." Today comets are thought to hold valuable clues to the origin of the Solar System, and some believe even the very water in our oceans and the carbon-based building blocks of life originated from comets. It is for this reason that comets are the focus of considerable research, culminating in the recent highly successful Rosetta mission to Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko. Within the last few decades large strides have been made in our understanding of comets, thanks to space missions to comet’s such as ESA’s Rosetta. ## A Brief Overview There are 3 components that make up an active comet. Firstly, the heart of the comet, the nucleus, which is solid core that contains the volatiles that fuel the comet. Then there is the coma, which is a cloud of rarefied gas and dust that forms around the nucleus. It is sometimes referred to as the head of the comet. Finally, there is a tail that trails in an anti-sunward direction from the coma. The following infographic gives an overview of those components. But we will examine the components in more interesting detail below.  ## Nucleus At the comet’s heart is the nucleus, a solid body typically 1-10km across made of a mixture of frozen gases, rock, dust and various carbon compounds. Common ices found on comet nuclei include water and Carbon Monoxide, however other ices have been found such as ammonia, ethane, methane, Carbon Dioxide and even ethanol. These ices help fuel the formation of a comet as nucleus approaches the sun. Thanks to various space missions as well as ground-based radar observations we have a fairly good idea about the size, shape and composition of comet nuclei. Here are some of the observations that have been made of comet nuclei. #### 1P/Halley On March 14, 1986, European Space Agency’s Giotto mission passed just 596km from the nucleus of the most famous comet of them all, Comet Halley. Because the comet was highly active, the spacecraft was showered with small debris as it approached, one impact spun the spacecraft off it’s axis another impact destroyed the main imaging camera! Luckily, before this happened Giotto was able to send back several good images. These images revealed the nucleus to very dark (darker than coal even) and peanut shaped with dimensions of 15km x 10km.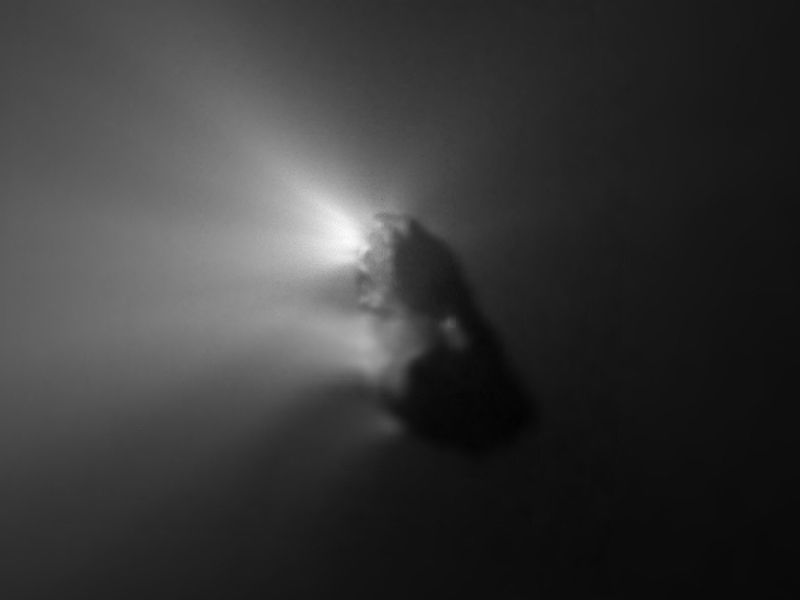  <center>*Giotto’s image (HMC68) of the nucleus of Halley’s Comet. Credit: ESA (European Space Agency)*</center> #### Comet 9P/Tempel NASA’s Deep Impact mission performed a rather unique experiment where they slammed a 300kg Copper projectile into the 8 x 5km nucleus of Comet Tempel as they monitored the effects of the impact. Several years later in 2011, NASA’s Stardust-NExT mission also performed a flyby of Comet Tempel that enabled it to image the area where the copper projectile had impacted in 2005. Based on the fact that the visible crater was flatter and more subsided that expected, scientists concluded that the comet nucleus was fragile and porous in nature. [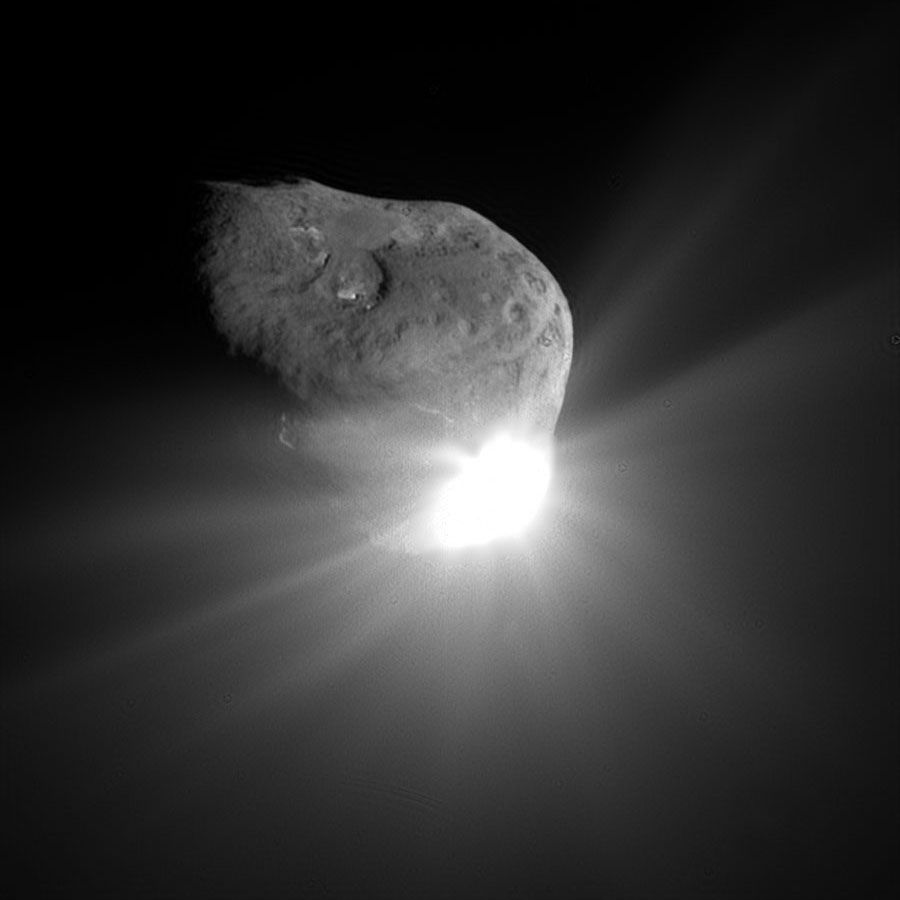](https://steemitimages.com/DQmXfmESLhpoiSPeLsRTGVGbRu3fSUYHNwfwmv2yVZiKej6/Tempel1-impact.gif) <center>*Please click image to view a movie of the actual impact*</center> <center>*The Deep Impact mission slammed a 300kg copper projectile into the nucleus of Comet Tempel on July 4, 2005. Image Credit:NASA*</center> #### 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko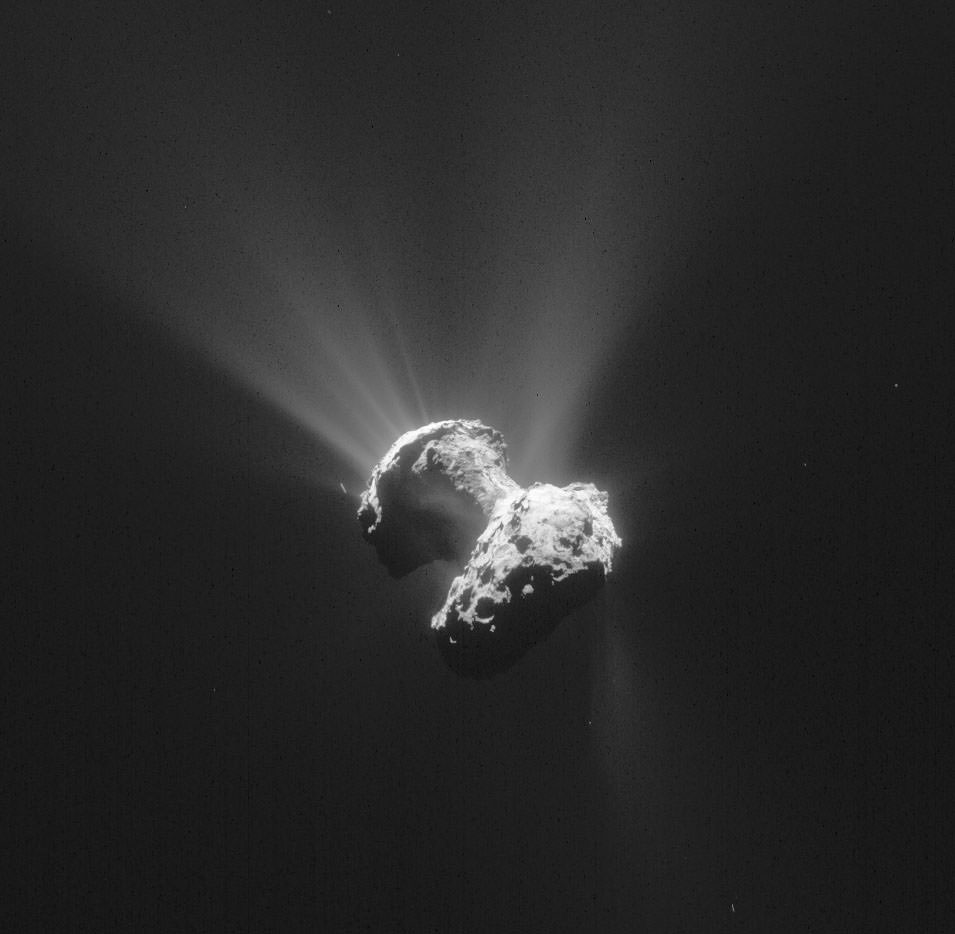  *Nucleus of Comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko. Copyright: ESA/Rosetta/NavCam* ESA sent their Rosetta spacecraft to Comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko where it monitored the comet continuously for over 2 years from 2014 to 2016. Our knowledge of comets grew enormously as a result. There were many interesting findings including that the ratio of deuterium to hydrogen in the water from the comet being significantly different to the earth. this has significant implications on theories of the origin of the solar system since the origin of terrestrial water would appear to be from a different source to the comet’s. ## Coma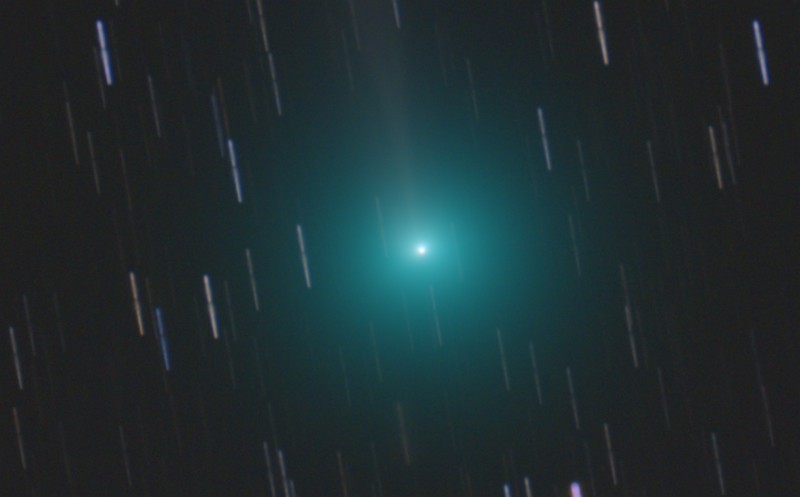  <center>*Coma of Comet C/2015 ER61 (PANSTARRS) fluoresces strongly green in the image from Apr 7, 2017. Image 210x8seconds with C14 f2 scope with QHY183c camera. Credit:Author*</center> When distant from the sun a comet looks like an asteroid, however, as it approaches the sun its surface begins to warm which in turns starts to sublimate its constituent ices which include Water, Carbon Dioxide and others. In the vacuum of space most ices sublimate, that is pass from the solid to gas phase without becoming a liquid. Because of outgassing dust and ice grains are also released, and these all combine to form a large cloud around the nucleus which typically extends 100,000 km or more, which is about the size of Jupiter. During the Rosetta mission it was found that Water and Carbon Dioxide liberated from the nucleus of Comet 67P were dissociated from free electrons, creating other products (like Diatomic Carbon and Hydrogen, among others). Often coma shine a vivid green, something some people can see even by direct observation by eye. Spectroscopic observations of coma reveal the main cause of this to be fluorescing diatomic carbon (C2) and Cyanogen (CN) which are presumably the byproduct of the dissociation of ices containing Carbon (CO2) and Nitrogen (Ammonia) from the nucleus surface. This can be seen in the following spectra which was obtained by renown French amateur astronomer Christian Buil. [For more information on Spectra and Spectroscopy please click on this link](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Astronomical_spectroscopy). I may well do a separate article on Astronomical Spectroscopy because it is quite fascinating and a lot of fun to do. 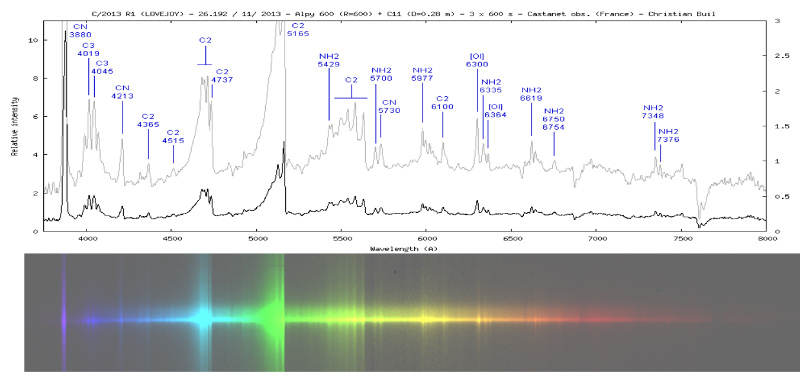 <center>*Comet Spectra. Observe how the C2 (Diatomic) has 2 bright emission lines in the green. Credit: Christian Buil*</center> Surround the nucleus and coma, but not visible in the visual spectrum is a large cloud of Hydrogen atoms, which extends well beyond the normal coma and most likely is derived from the dissociation of water from the nucleus. It can only be detected from outside the earth's atmosphere because of the wavelengths it emits. In the case of Comet Hale-Bopp in 1997 the Hydrogen envelope extended 1 Astronomical Unit, the distance between the sun and the earth! ## Comet Tails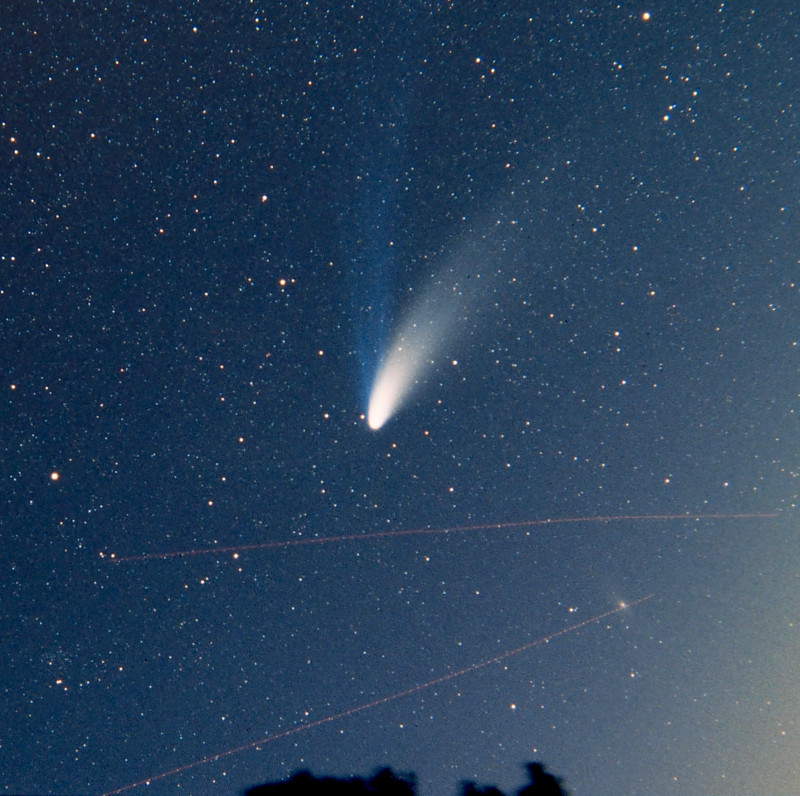  <center>*Comet Hale-Bopp’s distinctive white dust tail contrasts with the dimmer blue gas tail. The Andromeda Galaxy M31 is also visible bottom right of this image, as are 2 plane trails. This image was taken late March, 1997, from north of Los Angeles, Ca. Image Credit:Author*</center> The tail is the most well recognised feature of a comet, although often they are either absent or small. There are two main types of tails, the ion or gas tail and the dust tail. In very active comet’s like Comet Hale-Bopp in the image above both tails are strongly formed. #### Ion Tail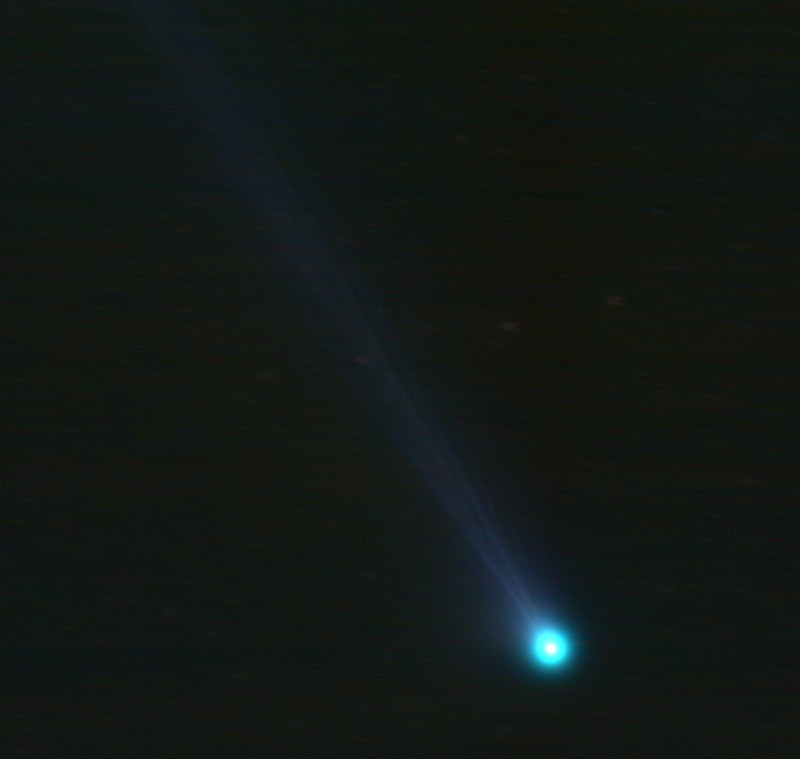  <center>*The blue ion tail in this image shines from Carbon Monoxide fluorescing. Solar wind rapidly drags the tail in the direction opposite the sun. Credit: Author* </center> As a comet gets closer to the sun it’s is subjected to greater heating which causes outgassing to increase. Additionally, some of the released gases begin to ionise and as these are charged, they are carried by the solar wind, a stream of charged particles from the sun, at velocities of the order of 500 km per second. This forms what is known as the ion tail, and it always points away from the sun because of the direction of the solar wind. Ionised CO (CO+) in the tail glows a distinctive blue color when the sun’s radiation causes it to fluoresce. #### Dust Tail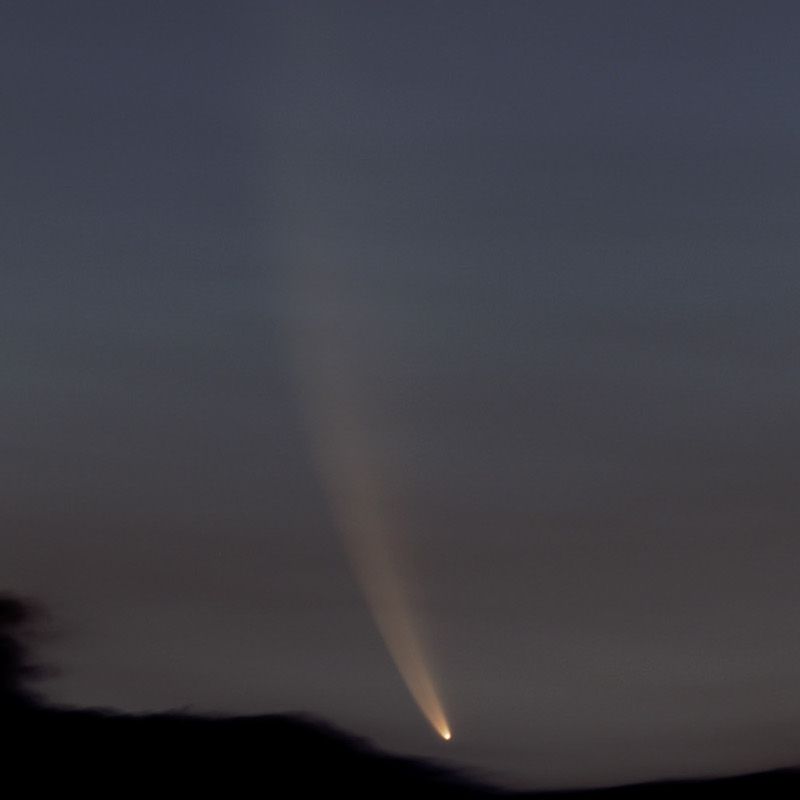  <center>*A classic curved dust tail (Comet McNaught in 2007). The tail is redden due to low elevation. Credit: Author*</center> Outgassing from the comet's nucleus also causes Dust and ice grains to be lifted off the nucleus are also pushed away from the sun, but the velocities are much lower than experienced with the ion tail so that the motion of the comet in it’s orbit can cause the tail to lag opposite to the comet’s motion. This causes the dust tail to form, which is essentially a broad sheet of dust that is more uniform and diffuse than an ion tail, and has an almost white color.  <center>*Comet Arend-Roland's dust tail in 1957 was viewed under unusual geometry which meant it could be seen in front of the comet as well. Credit:APPLAUSE*</center> ### Other types of tail Both Comet Hale-Bopp (1997) and Comet McNaught (2007) were both observed to have unusual tails made of Neutral Sodium atoms. The mechanism of formation for these is unknown. I was lucky to photograph the Sodium tail of Comet McNaught because I had a very clear sky (it is only one of 2 amateur photos I'm aware of that caught it)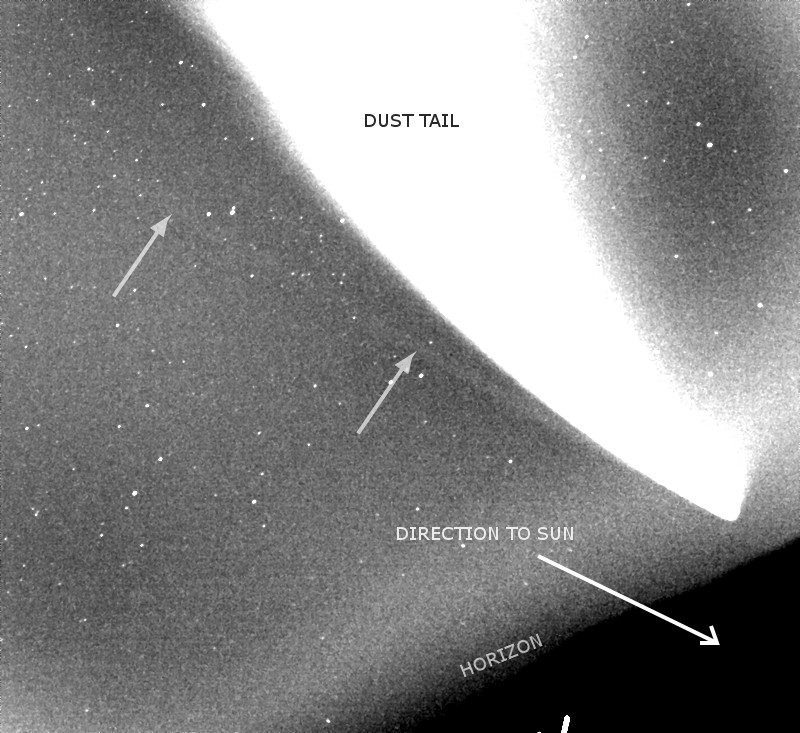  <center>*A highly contrast boosted photo Comet McNaught’s faint Neutral Sodium tail imaged by the author with a 200mm f2.8 lens and a 130 second exposure and a 350D on Jan 20, 2007. Only the red channel is shown. Credit: Author*</center> ## Orbits and Origins Unlike the planets which travel in near circular orbits in a similar plane to the earths, comets tend to have orbits that are much more elliptical and often quite inclined to the earths orbital plane. Halley’s Comet, for instance has an orbit that takes it close to within the orbit of Venus all the way out past Neptune’s orbit over a period of 76 years. A generic orbit is shown in the following diagram is typical of a comet like Halley. 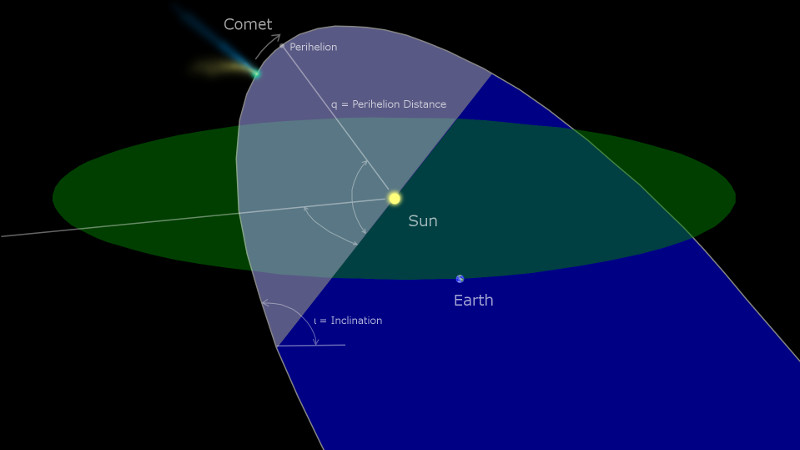 <center>*The orbit of a typical comet. Perihelion is the point at which the comet is closest the sun, and inclination is how tilted the orbit is relative to the plane of the earths*</center> Work done in 1950’s by astronomer Jan Oort demonstrated that a large population of comets have aphelia (most distant point from the sun) around the 50-200,000 AU distance. An AU is a measurement of distance equal to the sun to earth distance, or about 150,000,000 km. When these aphelion points are plotted they tend to describe a shell which we now call the Oort cloud as shown in the following diagram. It is postulated that an encounter with a nearby star can perturb comet’s inward towards the inner solar system. 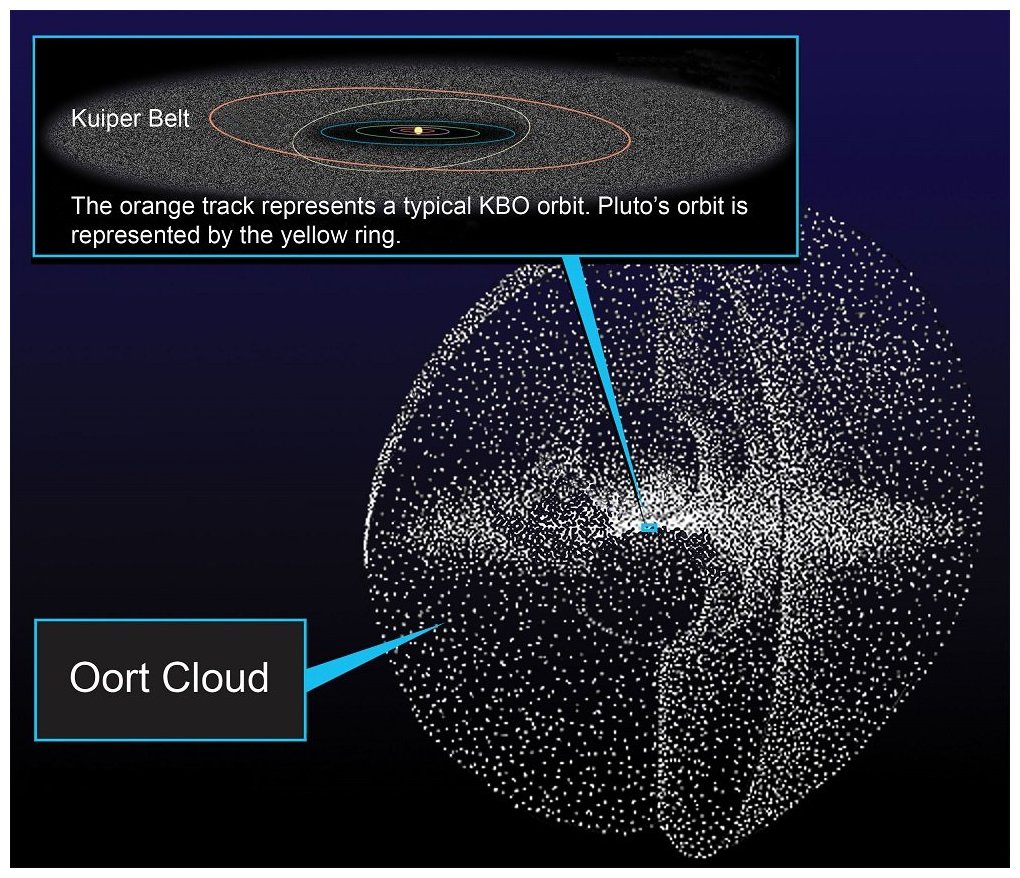 <center>*Image Credit Nasa*</center> One implication of the highly elliptical orbits of comets is the fact that a comet approaching the sun will encounter increasingly fierce solar radiation that changes at in inverse square law to the distance of the sun. Therefore, halving the distance to the sun means that solar radiation increases 4 times (2 squared). The result of this is that 4 times as much sunlight is being reflected/re-emitted from 4 times as much gas/dust, so the brightness of a comet will tend to increase as much as 16x for each halving of the solar distance (or at a inverse 4th power)! ## Conclusion This was a brief overview on the topic of comets. In the future I plan to do a number of additional articles including some information on how I came to discover a number of comets, as well as how professionals are interested in finding PHA's (potentially harmful asteroids). ## References 1. Magnani, Loris & F. Ahearn, M. (1986). CO/+ Fluorescence in Comets. Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. 97. . 10.1086/131694. 2. Oort, J. H. (1950).The structure of the cloud of comets surrounding the Solar System and a hypothesis concerning its origin. Bulletin of the Astronomical Institutes of the Netherlands, vol. 11, p. 91-110 (1950) 3. NASA Releases Images of Man-Made Crater on Comet. https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/stardust/news/stardust20110215.html
👍 opaulo, carlgnash, r-bot, shaka, yanakellen, remlaps2, cub2, bloom, ruth-girl, steemstem, lafona-miner, dna-replication, curie, liberosist, meerkat, roelandp, christianschmidt, hendrikdegrote, anwenbaumeister, locikll, kushed, spiry-btc, pharesim, alanzheng, kingsclot, tormiwah, maxdani, sy-gamsung, jamhuery, suesa, nonationnoborder, osmerj, lemouth, anarchyhasnogods, justtryme90, mobbs, the-devil, foundation, himal, lamouthe, rachelsmantra, nitesh9, kerriknox, gra, rockeynayak, rjbauer85, pearlumie, sci-guy, amavi, dber, gentleshaid, mystifact, kenadis, carloserp-2000, mountainwashere, hadji, fredrikaa, abigail-dantes, leczy, johnwjr7, boreas, proteus-h, mind-blowing, joseealvarezn, jnmarteau, firipinjin, otuama, btcsam, oddnimrod, darkwater1, leom1969, jagarmarten, ribbitingscience, sunflowers, singhbinod08, azissuloh, lorenzor, shammi8448, azlansugihen, misstyna, yahia13, lizaamran, mulyadedi, jakipatryk, hrj, twolittlebirds, daemon-nice, stabilowl,